What is pharmaceutical serialization?
Serialization is a system for verifying the authenticity of a drug between its release and its actual delivery to a patient. This method consists of putting a unique identifier on each box of medication in the form of a Data Matrix when it is released for distribution and loading all the identifiers of the boxes into a central database.
Source: The Serialization methodological guide, French Ministry of Solidarity and Health
Serialization of pharmaceutical products
What is a pharmaceutical product?
A pharmaceutical product is a product related to pharmacy. Pharmaceutical specialties are drugs that are industrially developed and exploited by pharmaceutical companies. A marketing authorization called “AMM” in French is required before they can be dispensed to patients. It should be noted that pharmaceutical products (preparations, specialties including drugs) may have distinct pharmaceutical appearances such as injectable solutions, oral solutions, tablets.
In Article L.5111-1 of the Public Health Code, a medicinal product is defined as “any substance or composition presented as having curative or preventive properties with respect to human or animal diseases, as well as any substance or composition that may be used in humans or animals or that may be administered to them, with a view to establishing a medical diagnosis or to restoring, correcting or modifying their physiological functions by exerting a pharmacological, immunological or metabolic action. »
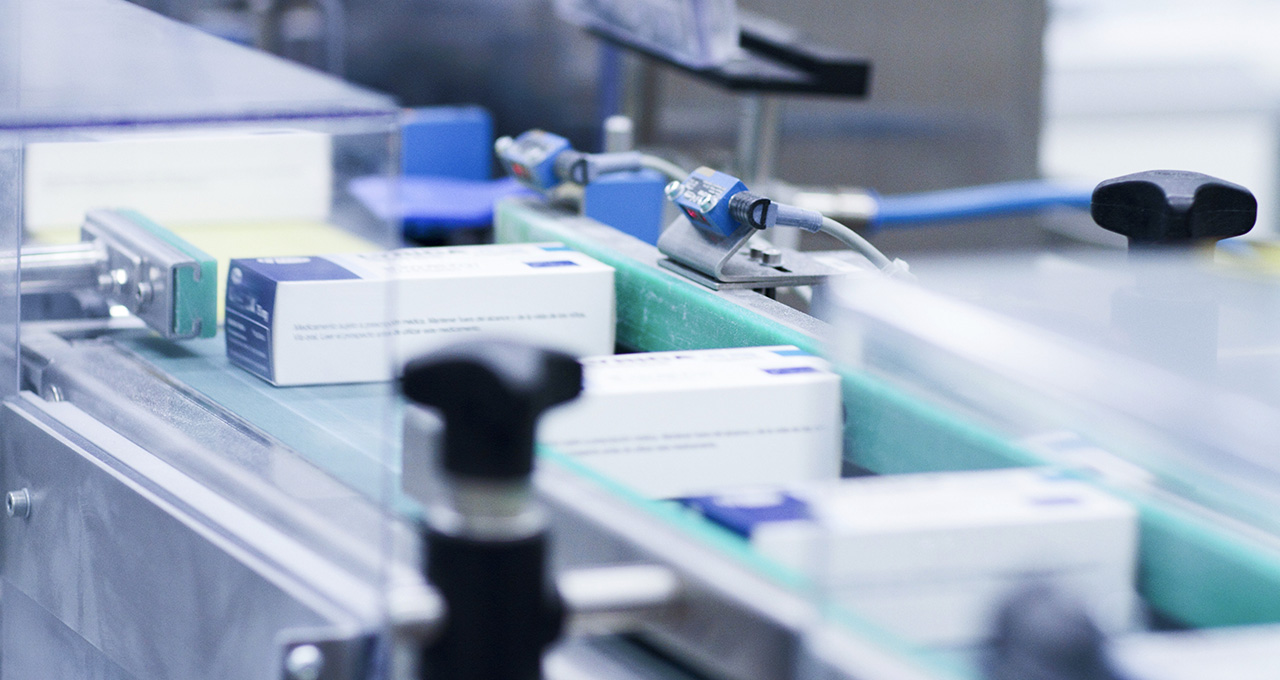

The serialization of pharmaceutical products: a major challenge
According to the World Health Organization (WHO), pharmaceuticals, including medicines, must be “safe, effective and of good quality”. The safety of pharmaceutical products is an important public health issue. Tracking and marking of pharmaceutical products is therefore necessary to offer a product with integrity, for example, not falsified. It is therefore necessary to mark and trace each case of medication.
How does the serialization of pharmaceutical products take place?
Serialization is a system for verifying the authenticity of drugs and pharmaceutical products between their distribution and their actual delivery to a patient. To do this, a unique identifier is placed on each box of medication when it is put into distribution. This information is then put into a central database. During the delivery to the patient, this identifier will be compared with the existing one in the database.
What are the necessary tools for the serialization of pharmaceutical products?
Serialization software enables to meet the regulatory requirements on serialization. One example is the Pharmacim LSM (Label serialization management) software suite developed by Courbon Software. Very complete, it includes several softwares for the steps of an optimal serialization such as the management of work orders and batches, serial numbers, printing control, line equipment piloting.
Pharmaceutical serialization in France and the European Union
How is pharmaceutical serialization piloted in the European Union?
The role of the EMVO
The European Medicines Verification Organization (EMVO) is a non-profit organization representing the actors in the legal distribution chain of medicines in Europe. EMVO is responsible for implementing the European Medicines Verification System (EMVS).
EMVS: European Medicines Verification System
This EMVO-led governance body has developed the model plan for national verification systems. This body complies with the characterizations of the FMD (European Directive on falsified medicinal products) and the DR (Delegated Regulation).
How is pharmaceutical serialization conducted at the national level?
It is the Delegated Regulation that sets the requirements for the system to be developed. However, its practical implementation and financing to the pharmaceutical sector is entrusted to the holders of a manufacturing authorization.
It should be noted that in each country of the member states of the European Union, a coordinating organization exists: the National Medical Verification Organization.
How is pharmaceutical serialization conducted in France?
France MVO: the French national governing body
He assumes the role of the National Medicine Verification Organisation (NMVO).
A national directory has been developed by France MVO to oversee and manage the directory system
Pharmaceutical serialization for the United States (USA)
The FDA (Food and Drug Administration), which is responsible for managing the approval and marketing of drugs in the United States.
This country has its own regulations. Standards are published and must be met. The FDA therefore has the power to make pharmaceutical products marketable in the USA. In terms of traceability, it is the use of the Datamatrix that is required: it must contain the national code of the drug, the serial number of the box, the batch number and the expiration date.
The FDA has a national directory of drug codes. It is reminded that the Drug Listing Act of 1972 requires registered pharmaceutical establishments to provide the FDA with an up-to-date list of all drugs manufactured, prepared, compounded or processed by it or for commercial distribution.
This administration indicates that pharmaceutical products are identified and reported using a unique three-segment number, with the National Drug Code (NDC) serving as the universal product identifier for drugs.
As the standard evolves on a regular basis, Courbon Software monitors regulatory requirements worldwide, including those of the United States, for pharmaceutical serialization.




